Perspectives: Electric Vehicles Infrastructure Edition
Accelerating towards a greener future with electric vehicles (EVs)
Unveiling the Potential of EVs in Southeast Asia
- EV adoption and opportunities within EV Infrastructure
- End-to-End and Charge Point Operators as the winning models within the space
- Southeast Asia as the next EV Infrastructure hub
Strong EV adoption drives E2W and Charging Infrastructure opportunities
Increasing demand for green transportation creates opportunities across high TAM sectors, namely Electric Two-Wheelers (E2W) and Charging Infrastructure.
EV adoption is driven by shifting preferences towards sustainable transport
Decarbonising the industry has emerged as a major global priority, with numerous countries pledging to intensify efforts in decarbonising public land transport. EV is a large industry with over $317 billion in market size, growing at 23.1% as seen in Fig. 1. This uptake is mainly driven by:
- Cost savings of up to 50% compared to petrol vehicles
- Government incentives and policies for increased EV adoption
- A favourable investment environment for sustainability initiatives
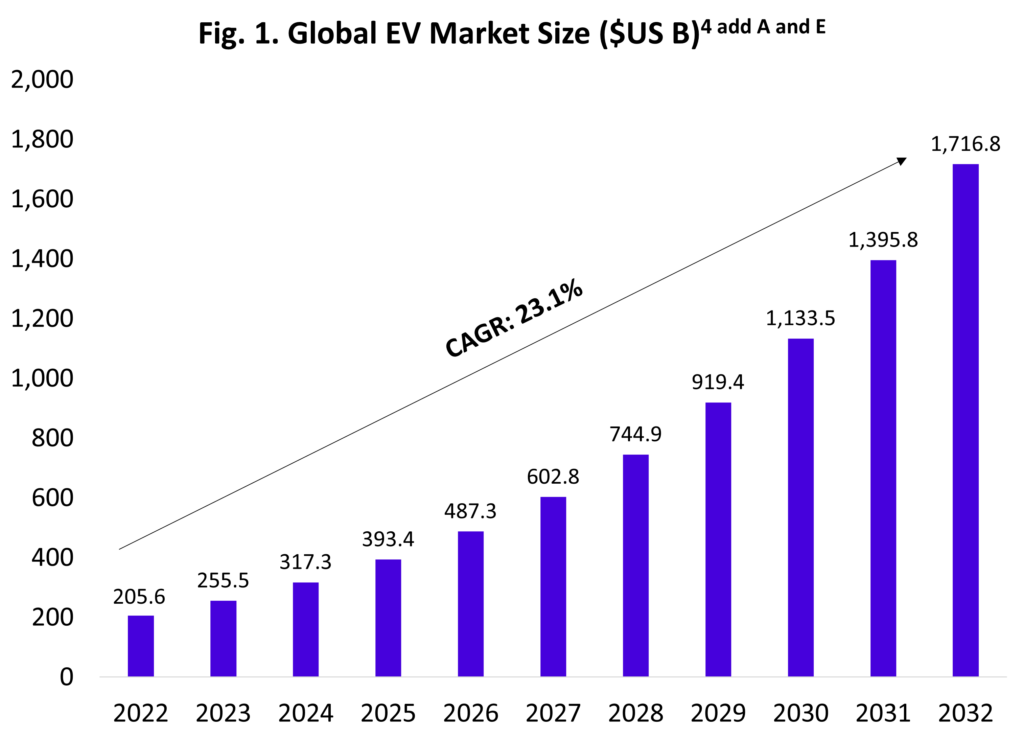
Developing proper infrastructure is crucial to meet both demand and adoption of EVs
With the ascent of EVs, the need for robust infrastructure becomes increasingly urgent. In Fig. 2., critical factors like Total Addressable Market (TAM), precedents, sector valuations, and funding were considered. Charging Infrastructure and E2W emerge as crucial sectors within the EV industry with high valuations, plenty of activity within the industry as seen by high funding trends and number of precedents. Fleets emerged as the least opportunistic sector, while E4W showed high valuations and funding but were found to be dominated by a few global player such as CVCs and conglomerates.
Fig. 2. EV Sectors Side-by-Side Analysis
| Sectors | No. of Unicorns | Total Valuation (US$ ‘000) | Total Funding Raised (US$ ‘000) | Opportunity in SEA |
| 1. Components & Materials | 2 | 16,328 | 3,280 | Low. No Expertise in SEA. |
| 2. Electric Four-Wheelers (E4W) | 5 | 945,942 | 32,200 | Low. Dominated by a Few Global Players. |
| 3. Electric Two-Wheelers (E2W) | 3 | 22,659 | 11,663 | High. Market opportunity present. |
| 4. Fleets | 0 | 1,914 | 142 | Mid. Opportunistic. |
| 5. Self-Operated/Third-Party Automobile Stores | Operated by E4Ws & Traditional Players | Low. No Relevant Players. | ||
| 6. Charging Infrastructure | 5 | 13,681 | 3,998 | High. Market opportunity present. |
| 7. Battery Swapping Stations | 1 | 1,992 | 232 | Low. No Clear Traction at the Moment. |
End-to-End EV Infrastructure and CPOs as winning models within the sector
High utilisation rates to achieve low capex and mitigate electricity and installation costs are crucial factors for EV infrastructure players.
Identifying the models in EV Infrastructure
Four primary models have surfaced in the EV infrastructure sector, covering the production, operation, and commercialization of EV chargers.
- Charge Point Operators (CPO): Operators of charging stations
- Charger OEMs: Producers of charging stations
- End-to-End (E2E): Produce and operate charging stations
- Technology: Provides charging management SaaS and consumer apps for chargers
Fig. 3. Overview of models within EV Infrastructure
| Business Models | Total Valuation | Total Funding | No. of Precedents | No. of Exits |
| 1. Charge Point Operators | $3.9B | $1.5B | 1 | 2 |
| 2. Charger OEMs | $92.8B | – | 2
*Traditional incumbents | – |
| 3. End-to-End | $9.7B | $2.4B | 4 | 5 |
| 4. Technology | $850M | $540M | 0 |
0 |
As depicted in Fig. 3, End-to-End (E2E) and Charge Point Operations (CPO) models have been identified to hold the most opportunity. Charger OEMs, despite high valuations, face challenges due to their need for specialized expertise, being less VC-backable, and their reliance on traditional players such as ABB, Schneider Electric, etc. that still generate majority of their business from non-EV products.
Key Success Factors to look out for in EV Infrastructure players in SEA
End-to-End and CPOs drive success through the following:
- Increasing Utilisation Rates: Has the ability to increase utilisation rates through strategies like optimising heat maps or providing fixed fee rentals to partners, similar to StarCharge and Bolt.Earth.
- Electricity and installation costs: Has the ability to breakeven on capex quickly by understanding installations and electricity costs .
- Scalable Partnerships: Collaborates with partners to identify sites with the highest utilisation to reduce capex such as fleets.
- Create a Charging Network Platform: Is able to integrate nation-wide charging points into a single platform.
| Charge Point | Star Charge | ||
| HQ | US | HQ | China |
| Market Cap | $839M
$2.4B Valuation at IPO | Valuation | $2.4B |
| Total Raised | $1.4B | Total Raised | $125M |
| Business Model | E2E Model | Business Model | E2E Model |
| Revenue Breakdown | 73% Charging Station
21% Subscriptions 6% Others | GTM Strategy | •Site selection for high utilisation rates
•Acquires smaller operator and offering cloud services |
EV Infrastructure gains regional momentum as successful players emerge
A sizable market, combined with appropriate regulations and facilities, sets the stage for sustainable transportation within the region.
Opportunities in Southeast Asia
Currently, the region’s EV market is valued at $1.5B, with an even greater CAGR of 32%.1 EV infrastructure is seeing a major boom in the region, presenting significant opportunities from the following developments:
- Availability of significant reserves of key raw materials for battery production.
- Growing infrastructure capacity, e.g. Increasing number of chargers in Thailand and Singapore.
- Favourable local adoption incentives such as tax reductions, subsidies, and convenient road access policies, etc.
- Most chargers are installed by private players and license for EV charging businesses are relatively easy to acquire.
As seen on Fig. 4 and Fig. 5, Singapore and Thailand emerge as the largest markets in Southeast Asia, boasting the highest number of chargers and highest TAM.
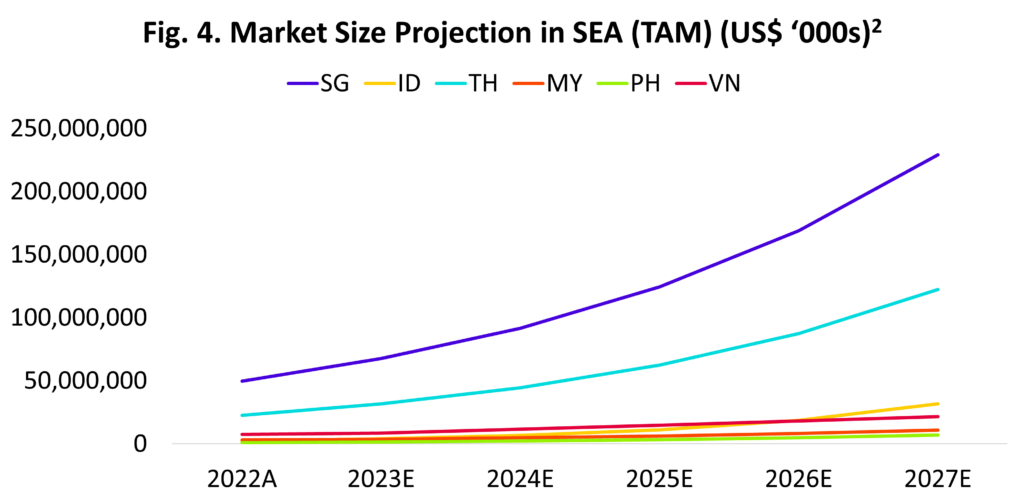
Fig. 5. EV Chargers in Southeast Asia
| No. of Chargers
(#) | 2022A | 2023E | 2024E |
| Singapore | 3,335 | 4,395 | 5,792 |
| Thailand | 3,739 | 5,184 | 7,188 |
| Vietnam | 2,000 | 2,286 | 3,070 |
| Malaysia | 898 | 1,085 | 1,404 |
| Indonesia | 440 | 875 | 1,424 |
| Philippines | 400 | 467 | 594 |
| Total | 10,813 | 14,292 | 19,473 |
| % Growth | 32% | 36% |
Key Takeaways for EV Infrastructure in SEA
- The EV market presents strong global and regional opportunities and is seeing rapid growth due to the increasing number of chargers, local adoption incentives, and significant private sector involvement, especially in SG and TH.
- E2E models and CPOs have the most significant opportunities for growth and high valuations within the EV infrastructure sector.
- Success in EV infrastructure is driven by high utilization rates, scalable partnerships, comprehensive charging network platforms, and dual charger installation for broad coverage and rapid expansion.
Author
Kristina Ticzon, Research Manager